前端必会数据结构与算法系列之树(六)
1. 什么是树
- 一种分层数据的抽象模型
- 前端工作中常见的树包括:DOM树、级联选择、树形控间
如下图级联选择器

我们用JS模拟一棵树
const tree = {
val: 'a',
children: [
{
val: 'b',
children: [
{
val: 'd',
children: [],
},
{
val: 'e',
children: [],
}
],
},
{
val: 'c',
children: [
{
val: 'f',
children: [],
},
{
val: 'g',
children: [],
}
],
}
],
};
链表是特殊化的树,树是特殊化的图(数据结构的存储方式只有两种:数组(顺序存储)和链表(链式存储)),摘自labuladong的算法小抄。
2. 树的常用操作
1. 深度优先搜索
- 尽可能深的搜索树的分支 步骤:
- 访问根节点
- 对根节点的 children 挨个进行深度优先遍历
如下图顺序
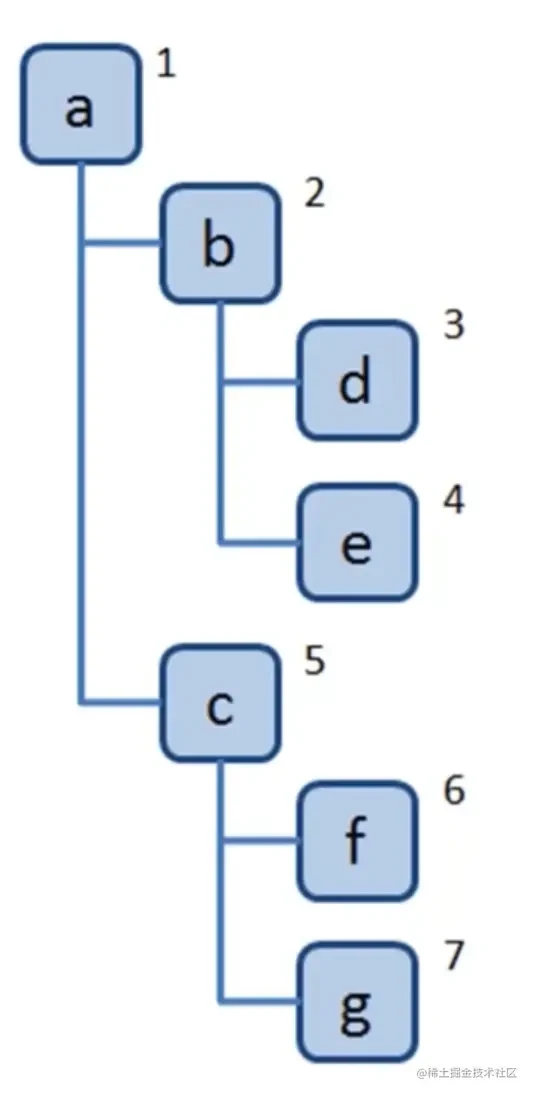
代码实现:
const dfs = root => {
console.log(root.val)
root.children.forEach(dfs)
}
2. 广度优先搜索
- 先访问离根节点最近的节点
步骤:
- 新建一个队列,把根节点入队
- 把队头出队并访问
- 把队头的 children 挨个入队
- 重复第二、三步,知道队列为空
如下图顺序:
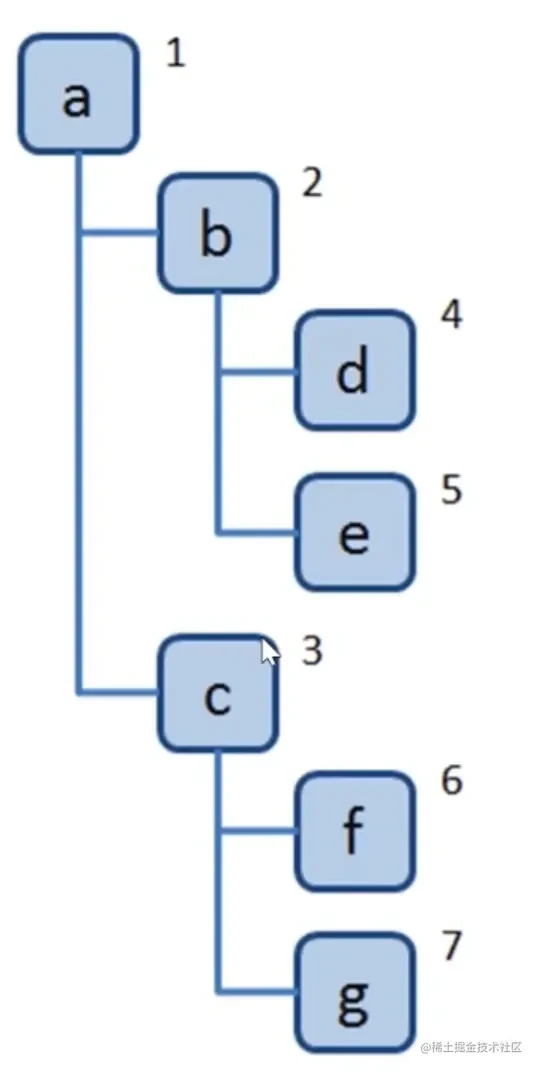
代码实现:
const bfs = (root) => {
const q = [root];
while (q.length > 0) {
const n = q.shift();
console.log(n.val);
n.children.forEach(child => {
q.push(child);
});
}
};
3. 二叉树和二叉搜索树
3.1 基本概念
二叉树是树中每个节点最多只能有两个子节点,一个是左侧子节点,另一个是右侧子节点。这个定义有助于我们写出更高效地在树中插入、查找和删除节点的算法。
现实中的二叉树:

模拟一个二叉树:
const bt = {
val: 1,
left: {
val: 2,
left: {
val: 4,
left: null,
right: null,
},
right: {
val: 5,
left: null,
right: null,
},
},
right: {
val: 3,
left: {
val: 6,
left: null,
right: null,
},
right: {
val: 7,
left: null,
right: null,
},
},
};
注意:当二叉树只有左子树或右子树时就成了链表
3.2 二叉树的遍历
二叉树的先、中、后序遍历其实就是深度优先遍历。
3.2.1 先序遍历(根左右)
- 访问根节点
- 对根节点的左子树进行先序遍历
- 对根节点的右子树进行先序遍历
先序遍历是以优先于后代节点的顺序访问每个节点的。先序遍历的一种应用是打印一个结构化的文档
先序遍历访问路径:
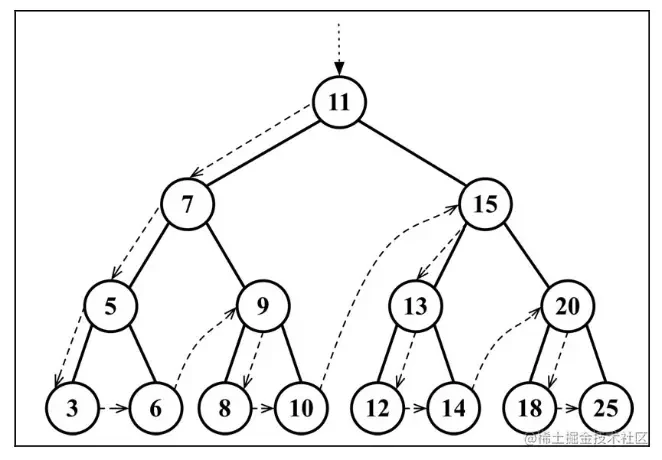
11 7 5 3 6 9 8 10 15 13 12 14 20 18 25
const preorder = (root) => {
if (!root) { return; }
console.log(root.val);
preorder(root.left);
preorder(root.right);
};
preorder(bt)
非递归版
const preorder = (root) => {
if (!root) { return; }
const stack = [root];
while (stack.length) {
const n = stack.pop();
console.log(n.val);
if (n.right) stack.push(n.right);
if (n.left) stack.push(n.left);
}
};
3.2.2 中序遍历(左根右)
- 对根节点的左子树进行中序遍历
- 访问根节点
- 对根节点的右子树进行中序遍历
二叉搜索树的中序遍历是一种以上行顺序访问 BST 所有节点的遍历方式,也就是以从最小到最大的顺序访问所有节点。中序遍历的一种应用就是对树进行排序操作
中序遍历访问路径:
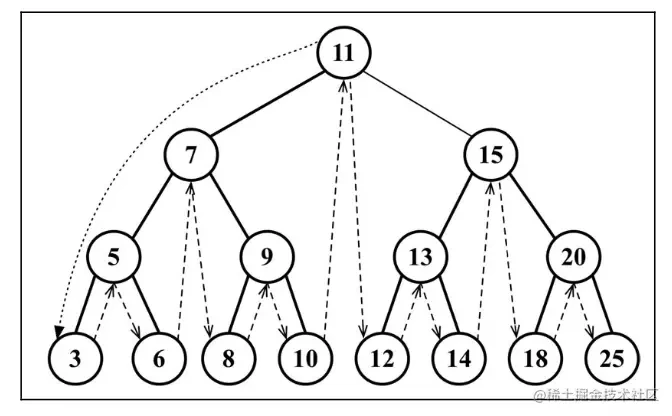
3 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 18 20 25
const inorder = (root) => {
if (!root) { return; }
inorder(root.left);
console.log(root.val);
inorder(root.right);
}
非递归版
const inorder = (root) => {
if (!root) { return; }
const stack = [];
let p = root;
while (stack.length || p) {
while (p) {
stack.push(p);
p = p.left;
}
const n = stack.pop();
console.log(n.val);
p = n.right;
}
};
3.2.3 后序遍历(左右根)
- 对根节点的左子树进行后序遍历
- 对根节点的右子树进行后序遍历
- 访问根节点
后序遍历则是先访问节点的后代节点,再访问节点本身。后序遍历的一种应用是计算一个目录及其子目录中所有文件所占空间的大小
后序遍历访问路径:
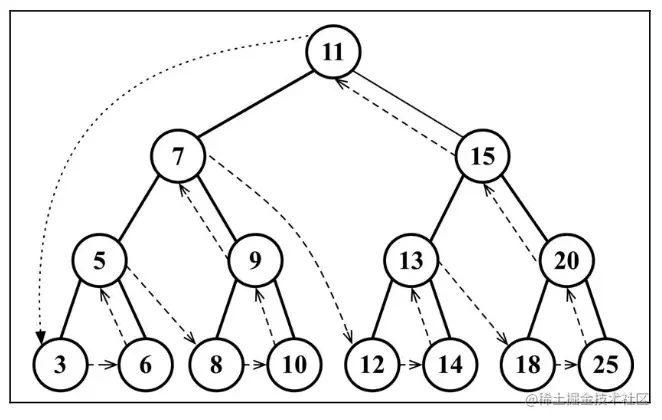
3 6 5 8 10 9 7 12 14 13 18 25 20 15 11
const postorder = (root) => {
if (!root) { return; }
postorder(root.left);
postorder(root.right);
console.log(root.val);
}
非递归版
const postorder = (root) => {
if (!root) { return; }
const outputStack = [];
const stack = [root];
while (stack.length) {
const n = stack.pop();
outputStack.push(n);
if (n.left) stack.push(n.left);
if (n.right) stack.push(n.right);
}
while(outputStack.length){
const n = outputStack.pop();
console.log(n.val);
}
};
3.3 二叉搜索树
3.3.1 基本概念
二叉搜索树(BST)是二叉树的一种,但是只允许你在左侧节点存储(比父节点)小的值, 在右侧节点存储(比父节点)大的值。
二叉搜索树数据结构的组织方式如下图:
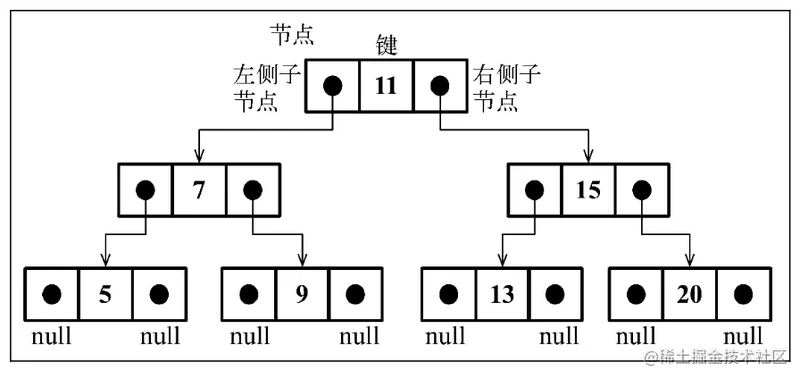
如下是一棵二叉搜索树
3.3.2 二叉搜索树代码实现
二叉树常用api:
insert(key): 向树中插入一个新的键。
search(key):在树中查找一个键。如果节点存在,则返回 true;如果不存在,则返回false。
inOrderTraverse():通过中序遍历方式遍历所有节点。
preOrderTraverse():通过先序遍历方式遍历所有节点。
postOrderTraverse():通过后序遍历方式遍历所有节点。
min():返回树中最小的值/键。
max():返回树中最大的值/键。
remove(key):从树中移除某个键
公共方法
class Node {
constructor(key) {
this.key = key;
this.left = undefined;
this.right = undefined;
}
toString() {
return `${this.key}`;
}
}
const Compare = {
LESS_THAN: -1,
BIGGER_THAN: 1,
EQUALS: 0
};
// 由于键可能是复杂的对象而不是数,我们使用传入二叉搜索树构造函数的 compareFn 函数来比较值
function defaultCompare(a, b) {
if (a === b) {
return Compare.EQUALS;
}
return a < b ? Compare.LESS_THAN : Compare.BIGGER_THAN;
}
class BinarySearchTree {
constructor(compareFn = defaultCompare) {
this.compareFn = compareFn; // 用来比较节点值
this.root = undefined; // 根节点
}
insert(key) {
if (this.root == null) { // 树为空
this.root = new Node(key);
} else {
this.insertNode(this.root, key);
}
}
insertNode(node, key) {
if (this.compareFn(key, node.key) === Compare.LESS_THAN) { // 小于根节点,左子树
// 递归
if (node.left == null) {
node.left = new Node(key);
} else {
this.insertNode(node.left, key);
}
} else if (node.right == null) { // 否则右子树递归
node.right = new Node(key);
} else {
this.insertNode(node.right, key);
}
}
getRoot() {
return this.root;
}
// 搜索特定值
search(key) {
return this.searchNode(this.root, key);
}
searchNode(node, key) {
if (node == null) {
return false;
}
if (this.compareFn(key, node.key) === Compare.LESS_THAN) { // 比当前节点小,在左子树搜索
return this.searchNode(node.left, key);
} else if (this.compareFn(key, node.key) === Compare.BIGGER_THAN) { // 比当前节点大,右子树搜索
return this.searchNode(node.right, key);
}
return true;
}
// 中序遍历(排序)
inOrderTraverse(callback) {
this.inOrderTraverseNode(this.root, callback);
}
inOrderTraverseNode(node, callback) {
if (node != null) {
this.inOrderTraverseNode(node.left, callback);
callback(node.key);
this.inOrderTraverseNode(node.right, callback);
}
}
// 先序遍历
preOrderTraverse(callback) {
this.preOrderTraverseNode(this.root, callback);
}
preOrderTraverseNode(node, callback) {
if (node != null) {
callback(node.key);
this.preOrderTraverseNode(node.left, callback);
this.preOrderTraverseNode(node.right, callback);
}
}
// 后序遍历
postOrderTraverse(callback) {
this.postOrderTraverseNode(this.root, callback);
}
postOrderTraverseNode(node, callback) {
if (node != null) {
this.postOrderTraverseNode(node.left, callback);
this.postOrderTraverseNode(node.right, callback);
callback(node.key);
}
}
// 获取最小值(左子树最下层)
min() {
return this.minNode(this.root);
}
minNode(node) {
let current = node;
while (current != null && current.left != null) {
current = current.left;
}
return current;
}
// 获取最大值(右子树最下层)
max() {
return this.maxNode(this.root);
}
maxNode(node) {
let current = node;
while (current != null && current.right != null) {
current = current.right;
}
return current;
}
// 移除节点
remove(key) {
this.root = this.removeNode(this.root, key);
}
removeNode(node, key) {
if (node == null) {
return undefined;
}
// 找到要移除的键
if (this.compareFn(key, node.key) === Compare.LESS_THAN) {
node.left = this.removeNode(node.left, key);
return node;
} else if (this.compareFn(key, node.key) === Compare.BIGGER_THAN) {
node.right = this.removeNode(node.right, key);
return node;
}
// 没有叶节点,直接修改值为undefined
if (node.left == null && node.right == null) {
node = undefined;
return node;
}
// 有一个子节点,跳过该节点,直接将父节点指向它的指针指向子节点
if (node.left == null) {
node = node.right;
return node;
} else if (node.right == null) {
node = node.left;
return node;
}
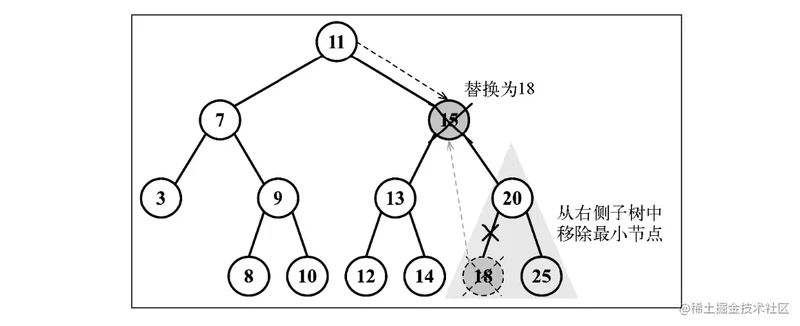
// 有两个子节点
// 1. 找到它右边子树中最小的节点
const aux = this.minNode(node.right);
// 2. 用它右侧子树中最小节点的键去更新这个节点的值(移除)
node.key = aux.key;
// 3. 右侧子树中的 最小节点移除
node.right = this.removeNode(node.right, aux.key);
// 4. 向它的父节点返回更新后节点的引用
return node;
}
}
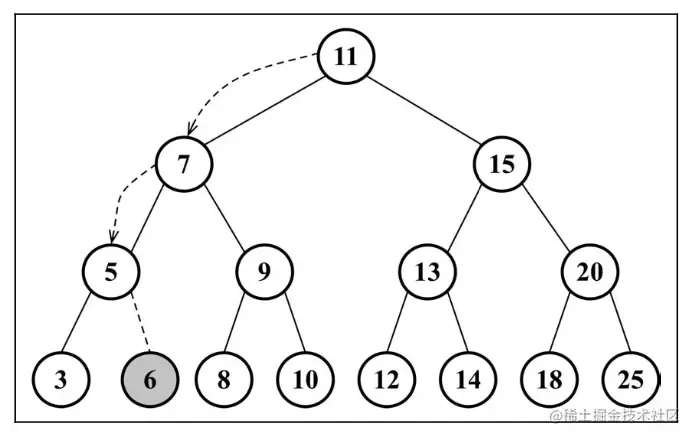
移除叶节点过程:
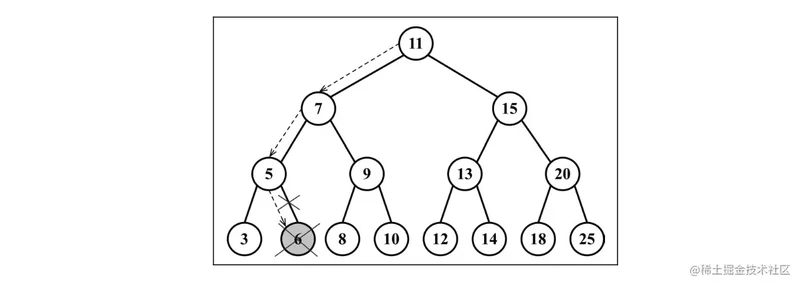
移除有一个左侧或右侧子节点的节点过程:
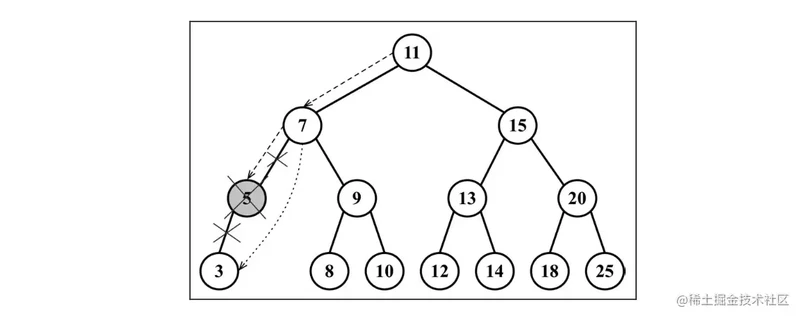
移除有两个子节点的节点过程:
树常用操作的时间复杂度分析:visualgo.net/zh/bst
4. 自平衡树
后续高级树章节再讲。
5. 树的常见应用
5.1 遍历JSON所有节点值
使用深度优先搜索
const json = {
a: { b: { c: 1 } },
d: [1, 2],
};
const json = {
a: { b: { c: 1 } },
d: [1, 2],
};
const dfs = (n, path) => {
console.log(n, path);
Object.keys(n).forEach(k => {
dfs(n[k], path.concat(k));
});
};
dfs(json, []);
5.2 渲染Antd 的树组件
const { Tree } = antd;
const { TreeNode } = Tree;
const json = [
{
title: '一',
key: "1" ,
children: [{ title: "三", key: "3", children: [] } ]
},
{
title: '二',
key: "2" ,
children: [{ title: "四", key: "4", children: [] } ]
}
];
class Demo extends React.Component {
dfs = n => {
return (
<TreeNode title={n.title} key={n.key}>
{n.children.map(this.dfs)}
</TreeNode>
)
}
render() {
return (
<Tree>
{json.map(this.dfs)}
</Tree>
)
}
}
ReactDom.render(<Demo />, mountNode)
6. leetcode常见考题
6.1 easy
1. 二叉树的最大深度
难度:简单
题解:二叉树的最大深度 DFS/BFS
2. 二叉树的最小深度
难度:简单
题解:二叉树的最小深度 BFS/DFS
3. 路径总和
难度:简单
题解:路径总和 DFS
4. N 叉树的前序遍历
难度:简单
题解:N 叉树的前序遍历(递归/迭代)
5. N 叉树的后序遍历
难度:简单
题解:N 叉树的后序遍历(迭代/递归)
6. N 叉树的层序遍历
难度:中等
题解:N 叉树的层序遍历
7. 相同的树
难度:简单
题解:相同的树DFS
8. 对称二叉树
难度:简单
题解:对称二叉树(递归法,迭代法)
9. 翻转二叉树
难度:简单
题解:翻转二叉树(递归/迭代)
6.2 medium
1. 二叉树的层序遍历
难度:中等
题解:二叉树的层序遍历BFS
2. 二叉树的前序遍历
难度:中等
题解:二叉树的前序遍历(递归/迭代)
3. 二叉树的中序遍历
难度:中等
题解:二叉树的中序遍历(递归/迭代)
4. 二叉树的后序遍历
难度:简单
题解:# 二叉树的后序遍历(递归/迭代)
5. 验证二叉搜索树
难度:中等
题解:验证二叉搜索树(递归与中序遍历)
6. 二叉搜索树中的插入操作
难度:中等
题解:二叉搜索树插入操作
7. 删除二叉搜索树中的节点
难度:中等
题解:删除二叉树中的节点
8. 完全二叉树的节点个数
难度:中等
题解:完全二叉树的节点个数
9. 二叉树的最近公共祖先
难度:中等
题解:二叉树的最近公共祖先(后序遍历)
10.在每个树行中找最大值
难度:中等
题解:在每个树行中找最大值(BFS)
11.从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
难度:中等
题解:从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
12. 递归树结构数据查找节点,并输出从根到该节点的路径
let arrPath = [] // 保存路径
let count = 0
function deepFinds(node, target) {
arrPath.push(node.value)
if (node.value === target) {
count++
}
if(node.children) {
for (let i = 0; i < node.children.length; i++) {
let flag = deepFinds(node.children[i], target)
if (!flag) {
arrPath.pop()
} else {
break
}
}
}
return count > 0
}
deepFinds(tree, "A321")
tree数据
let tree = {
value: "A",
children: [
{
value: "A1",
children: [
{
value: "A11",
},
{
value: "A12",
},
],
},
{
value: "A2",
children: [
{
value: "A21",
},
{
value: "A22",
},
],
},
{
value: "A3",
children: [
{
value: "A31",
},
{
value: "A32",
children: [
{
value: "A321",
},
],
},
],
},
],
}
13. 扁平数据结构转Tree
let arr = [
{id: 1, name: '部门1', pid: 0},
{id: 2, name: '部门2', pid: 1},
{id: 3, name: '部门3', pid: 1},
{id: 4, name: '部门4', pid: 3},
{id: 5, name: '部门5', pid: 4},
]
转为
[
{
"id": 1,
"name": "部门1",
"pid": 0,
"children": [
{
"id": 2,
"name": "部门2",
"pid": 1,
"children": []
},
{
"id": 3,
"name": "部门3",
"pid": 1,
"children": [
// 结果 ,,,
]
}
]
}
]
解法1: 递归
const getChildren = (data, result, pid) => {
for (const item of data) {
if (item.pid === pid) {
const newItem = { ...item, children: [] };
result.push(newItem);
// 获取当前节点的子节点
getChildren(data, newItem.children, item.id);
}
}
}
const arrayToTree = (data) => {
const result = [];
// 获取根节点(父节点为0)
getChildren(data, result, 0)
return result;
}
解法2: 迭代加Map
function arrayToTree(items) {
const result = []; // 存放结果集
const itemMap = {};
// 先转成map存储
for (const item of items) {
itemMap[item.id] = { ...item, children: [] }
}
for (const item of items) {
const id = item.id;
const pid = item.pid;
const treeItem = itemMap[id];
if (pid === 0) { // 根节点
result.push(treeItem);
} else {
if (!itemMap[pid]) { // 没有找到父节点,新建一个空父节点
itemMap[pid] = {
children: [],
}
}
// 加入父节点children中
itemMap[pid].children.push(treeItem)
}
}
return result;
}
优化一次遍历:比较难懂,复杂度还是O(n)
function arrayToTree(items) {
const result = []; // 存放结果集
const itemMap = {};
for (const item of items) {
const id = item.id;
const pid = item.pid;
if (!itemMap[id]) {
itemMap[id] = {
children: [],
}
}
// map存储
itemMap[id] = {
...item,
children: itemMap[id]['children']
}
const treeItem = itemMap[id];
if (pid === 0) {
result.push(treeItem);
} else {
if (!itemMap[pid]) {
itemMap[pid] = {
children: [],
}
}
itemMap[pid].children.push(treeItem)
}
}
return result;
}
原文地址:juejin.cn/post/698390…
6.3 hard
1. 二叉树的序列化与反序列化
难度:困难
题解:二叉树的序列化与反序列化(多解法)
